How to use AWS Secrets Manager in Airflow
Datacoves integrates with the Airflow Secrets Backend Interface, offering support for both its native Datacoves Secrets Backend and AWS Secrets Manager. For other Airflow-compatible Secrets Managers, please reach out to us.
Secrets backends are configured per project. See configure your AWS Secrets Manager for details.
Read variable from AWS Secrets Manager
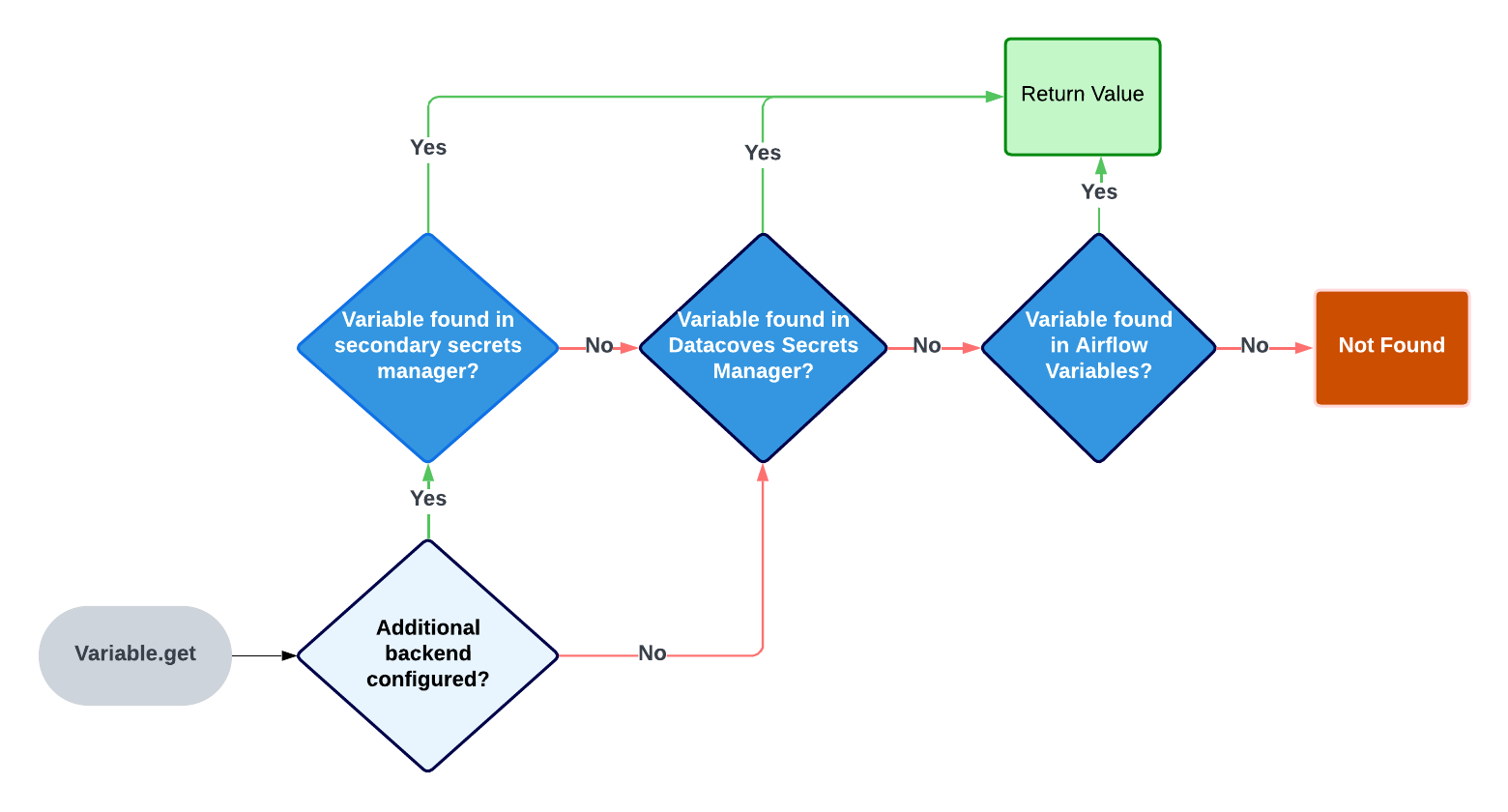
Airflow's Variable.get searches multiple places:
- AWS Secrets Manager (if configured)
- Datacoves Secrets Manager
- Airflow environment variables
Once a variable is found, Airflow stops searching.
Best practices
- Call
Variable.getfrom within an Airflow/Datacoves decorator to fetch at runtime only. - Use
connections_lookup_patternandvariables_lookup_patternto filter prefixes (e.g.,aws_) to reduce unnecessary API calls. Example:aws_my_secret.
Example DAG using AWS Secrets Manager
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.models import Variable
@dag(
catchup=False,
default_args={
"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1),
"owner": "Mayra Pena",
"email": "mayra@example.com",
"email_on_failure": True,
},
tags=["version_1"],
description="Testing task decorators",
schedule_interval="0 0 1 */12 *",
)
def task_decorators_example():
@task.datacoves_bash(connection_id="main")
def calling_vars_in_decorator() -> str:
my_var = Variable.get("aws_my_secret")
return "My variable is: " + my_var
calling_vars_in_decorator()
dag = task_decorators_example()
To auto mask your secret you can use secret or password in the secret name since this will set hide_sensitive_var_conn_fields to True. eg aws_my_password. Please see this documentation for a full list of masking words.
Using a secrets manager directly from Airflow
While not recommended, you can bypass the Datacoves secrets manager integration by configuring an Airflow connection and using the SecretsManagerHook in an Airflow DAG.
Configure an Airflow Connection
Create a new Airflow Connection with the following parameters:
Connection Id: aws_secrets_manager
Connection Type: Amazon Web Services
AWS Access Key ID: ....
AWS Secret Access Key: ....
Extra:
{
"region_name": "us-west-2"
}
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.providers.amazon.aws.hooks.secrets_manager import SecretsManagerHook
@dag(
catchup=False,
default_args={
"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1),
"owner": "Noel Gomez",
"email": "noel@example.com",
"email_on_failure": True,
},
tags=["sample"],
description="Testing task decorators",
schedule_interval="0 0 1 */12 *",
)
def variable_usage():
@task.datacoves_bash
def aws_var():
secrets_manager_hook = SecretsManagerHook(aws_conn_id='aws_secrets_manager')
var = secrets_manager_hook.get_secret("airflow/variables/aws_ngtest")
return f"export MY_VAR={var} && echo $MY_VAR"
aws_var()
dag = variable_usage()
Check when secret is being fetched from AWS
It is a good idea to verify that Secrets are only being fetched when expected. To do this, you can use AWS CloudTrail.
- From the AWS Console, go to
CloudTrail - Click
Event History - Click
Clear Filter - In the
Lookup Attributesdropdown, selectEvent Name - In the
Enter an Event Nameinput box, enterGetSecretValue
Review the Resource name and Event time.
Note: it may take a few minutes for fetch events to show up in CloudTrail.