How to use AWS Secrets Manager in Airflow
Datacoves integrates with the Airflow Secrets Backend Interface, offering seamless support for both its native Datacoves Secrets Backend and AWS Secrets Manager. If you’re interested in using additional Airflow-compatible Secrets Managers, please reach out to us.
Secrets backends are configured at the project level, this means that you can use a different Secrets Manager for each project. Please see additional documentation to configure your AWS Secrets Manager
Read variable from AWS Secrets manager
When using
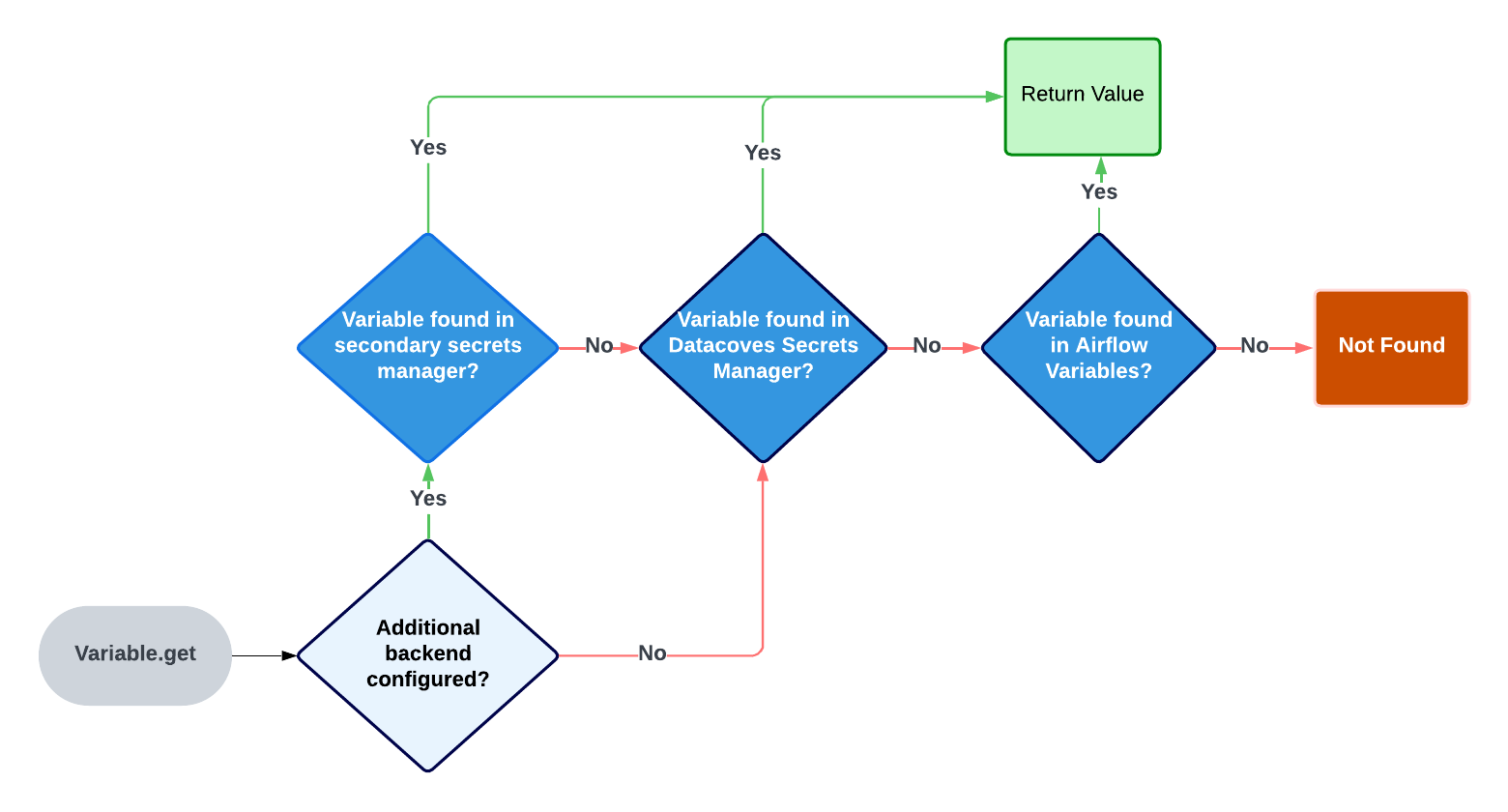
Variable.get
Airflow will look in several places to find the variable.
The order of places it will look for are as follows:
- AWS Secrets Manager (If this is configured as seen above)
- Datacoves Secrets Manager
- Airflow environment variables
Once a variable is found Airflow will stop its search.
Each time a variable is accessed, an API call is made to AWS Secrets Manager. If not configured properly, this API call may occur every time a DAG is parsed (every 30 seconds), not just during task execution. Since AWS is the first place Airflow looks for variables, repeated calls can significantly increase API usage and lead to a higher-than-expected AWS bill. You can read more about this here .
To solve for this there are 2 best practices to follow:
-
Always call your
Variable.getfrom within an Airflow decorator such as the Datacoves Bash Task Decorator. This ensures the variable is only fetched at run time. -
Make use of the
connections_lookup_patternandvariables_lookup_patternwhen setting up your secondary backend above. This means only variables and connections prefixed withaws_would be make an API call to AWS Secrets Manager. eg)aws_my_secret
"""
## Sample DAG using variables
This DAG is a sample using the Datacoves decorators with variable from AWS.
"""
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.models import Variable
@dag(
doc_md = __doc__,
catchup = False,
default_args={
"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1),
"owner": "Mayra Pena",
"email": "mayra@example.com",
"email_on_failure": True,
},
tags=["version_1"],
description="Testing task decorators",
schedule_interval="0 0 1 */12 *",
)
def task_decorators_example():
@task.datacoves_bash(connection_id="main")
def calling_vars_in_decorators() -> str:
my_var = Variable.get("aws_my_secret") # Call variable within @task.datacoves_bash
return f"My variable is: {my_var}"
calling_vars_in_decorator() # Call task function
# Invoke Dag
task_decorators_example()
Tip
To auto mask your secret you can use
secretorpasswordin the secret name since this will sethide_sensitive_var_conn_fieldsto True. eg) aws_my_password. Please see this documentation for a full list of masking words.
Using a secrets manager directly from Airflow
While not recommended, you can bypass the Datacoves secrets manager integration by configuring an Airflow connection and using the
SecretsManagerHook
in an Airflow DAG.
Configure an Airflow Connection
Create a new Airflow Connection with the following parameters:
Connection Id: aws_secrets_manager Connection Type: Amazon Web Services AWS Access Key ID: .... AWS Secret Access Key: .... Extra: { "region_name": "us-west-2" }
"""
## Sample DAG using variables
This DAG is a sample using the Datacoves decorators with variable from AWS.
"""
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.providers.amazon.aws.hooks.secrets_manager import SecretsManagerHook
@dag(
doc_md = __doc__,
catchup = False,
default_args={
"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1),
"owner": "Noel Gomez",
"email": "noel@example.com",
"email_on_failure": True,
},
tags=["sample"],
description="Testing task decorators",
schedule_interval="0 0 1 */12 *",
)
def variable_usage():
@task.datacoves_bash
def aws_var():
secrets_manager_hook = SecretsManagerHook(aws_conn_id='aws_secrets_manager')
var = secrets_manager_hook.get_secret("airflow/variables/aws_ngtest")
return f"export MY_VAR={var} && echo $MY_VAR"
aws_var()
variable_usage()
Check when secret is being fetched from AWS
It is a good idea to verify that Secrets are only being fetched when expected. To do this, you can use AWS CloudTrail.
-
From the AWS Console, go to
CloudTrail -
Click
Event History -
Click
Clear Filter -
In the
Lookup Attributesdropdown, selectEvent Name -
In the
Enter an Event Nameinput box, enterGetSecretValue
Review the
Resource name
and
Event time
.
Note: it may take a few minutes for fetch events to show up in CloudTrail.