Variables and Connections
Note
dbt-coves generate airflow-dags does not support reading variables/connections, but you may generate the initial Python Airflow DAG and add the connection / variable information.
The best way to store and retrieve information within Airflow is to use
Variables
and
Connections
, both available on the
Admin
upper dropdown.
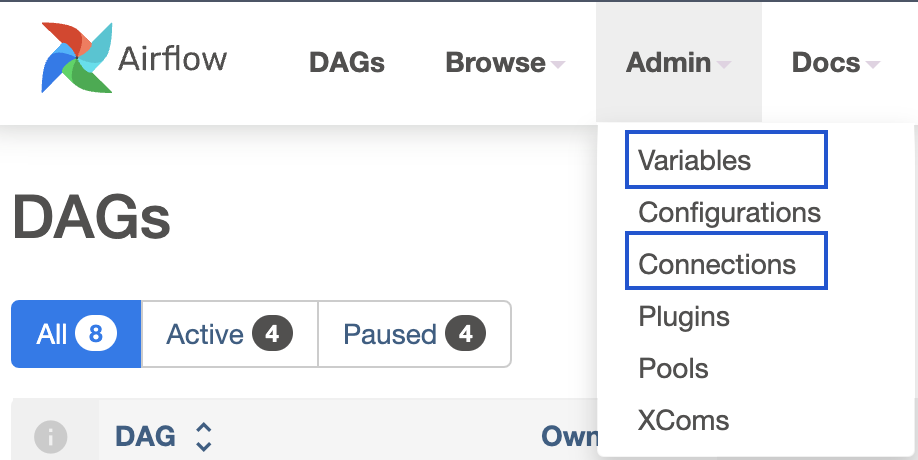
The main difference between them is that Variables is a generic multi-purpose store, while Connections are aimed at third-party providers.
Tip
Rather than using connections or variables stored in Airflow’s database, we recommend using a Secrets Manager. These secrets are encrypted and can be stored either in Datacoves Secrets manager or a third-party secrets manager like AWS Secrets Manager
Usage
Variables
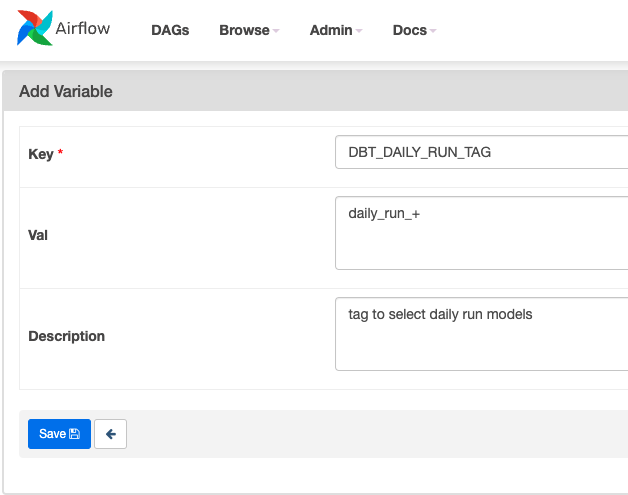
After creating a variable in Airflow's UI, using it is as simple as importing the
Variable
model in your DAG and
getting
it's name. If a variable contains
SECRET
on it's name, value will be hidden:
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from airflow.models import Variable
@dag(
default_args={"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1)},
description="DAG that outputs a Variable",
schedule="0 0 1 */12 *",
tags=["version_1"],
catchup=False,
)
def variables_dag():
@task.datacoves_bash(="main")
def transform():
daily_run_tag = Variable.get("DBT_DAILY_RUN_TAG")
return f"dbt build -s 'tag:{daily_run_tag}'"
transform()
variables_dag()
Connections
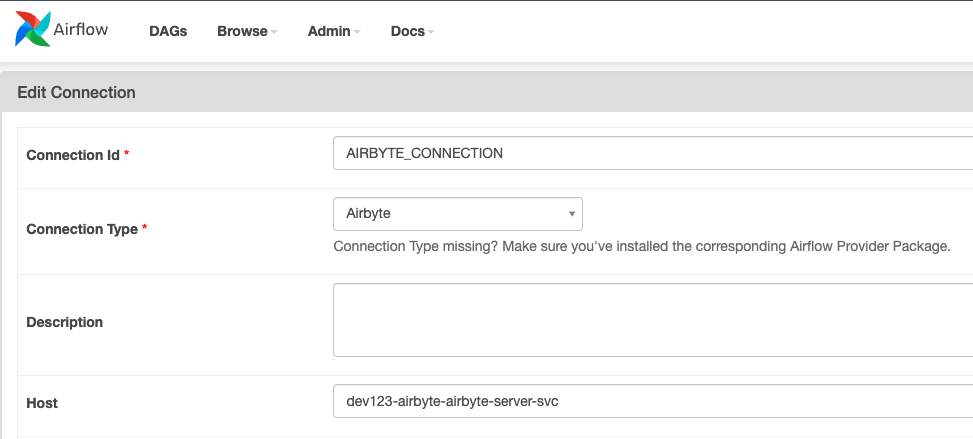
Consuming connections data is also straightforward, though you need to take it's attributes into consideration, as they'll vary depending on the provider.
In the following example, a connection of
type Airbyte
is created, and it's
host
is echoed in a DAG.
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from airflow.models import Connection
@dag(
default_args={"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1)},
description="DAG that outputs Airbyte Hostname",
schedule="0 0 1 */12 *",
tags=["version_1"],
catchup=False,
)
def connections_dag():
@task.datacoves_bash()
def echo_airbyte_host():
airbyte_connection = Connection.get_connection_from_secrets(conn_id="AIRBYTE_CONNECTION")
return f"echo 'Airbyte hostname is {airbyte_connection.host}'"
echo_airbyte_host()
connections_dag()