How to add Warehouses, Schemas, and Roles to Snowflake
Since we want all changes to the warehouse to be driven by code, we employ Permifrost and some additional scripts to manage changes to Snowflake. (contact us for assistance configuring your repository with the additional scripts needed)
Using Permifrost Configuration Files, we will manage the following:
- Warehouse Creation
- Schema Creation
- Role Creation
We will also need to configure dbt to use custom schemas by updating
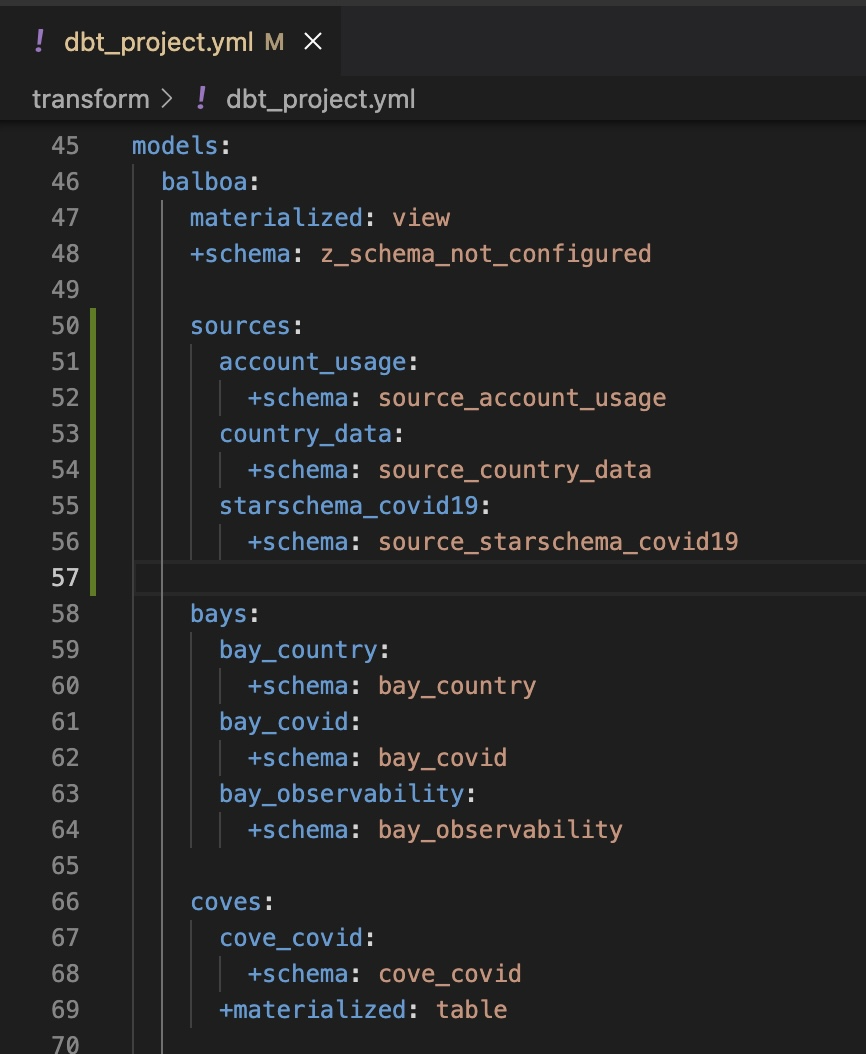
dbt_project.yml
create_snowflake_objects.py
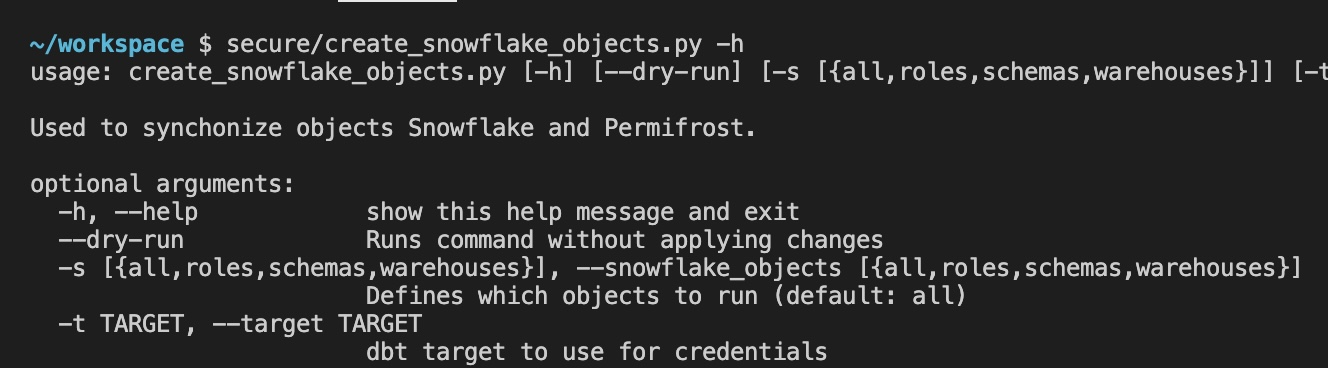
To create objects in Snowflake, we leverage a script we created
create_snowflake_objects.py
. This script uses the permifrost config files and dbt to apply the changes to Snowflake. Note: When you run these scripts your user will need to have the SYSADMIN or SECURITYADMIN to create specific objects in Snowflake.
Warehouse Creation
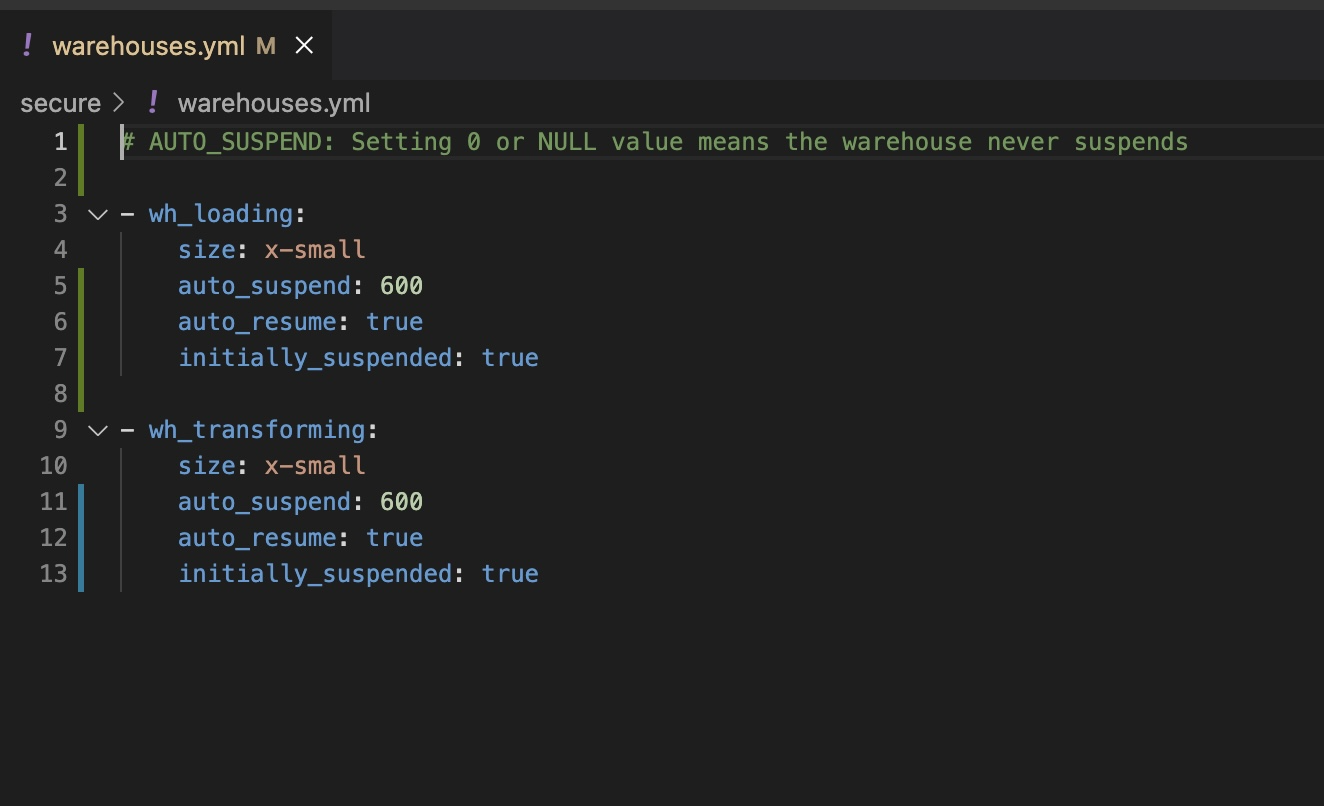
In the
secure/
folder of your repo, find the
warehouses.yml
file. Configure each warehouse you want to create in Snowflake.
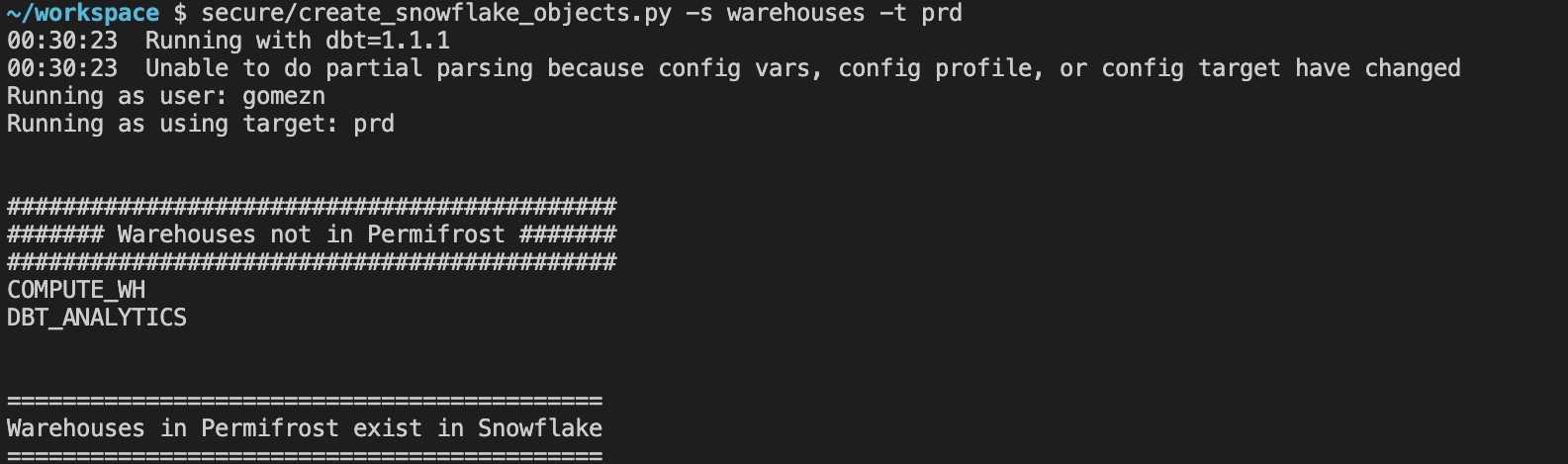
Once the
warehouses.yml
file is configured run
secure/create_snowflake_objects.py -s warehouses -t prd
to create the warehouses using your dbt
prd
target for authentication.
You can use the
--dry-run
option to see the expected changes before they are applied to Snowflake.
The script will also report objects that exist in Snowflake but which are missing from the
warehouses.yml
configuration file. If no changes are needed in Snowflake because the warehouse already exists, this will also be displayed.
Schema Creation
Schema creation is similar to warehouse creation. Schemas are configured in
secure/databases.yml
and the
secure/create_snowflake_objects.py -s schemas -t prd
command is run to create them. Note this script should run with the same role that normally runs your dbt jobs like
TRANSFORMER_DBT
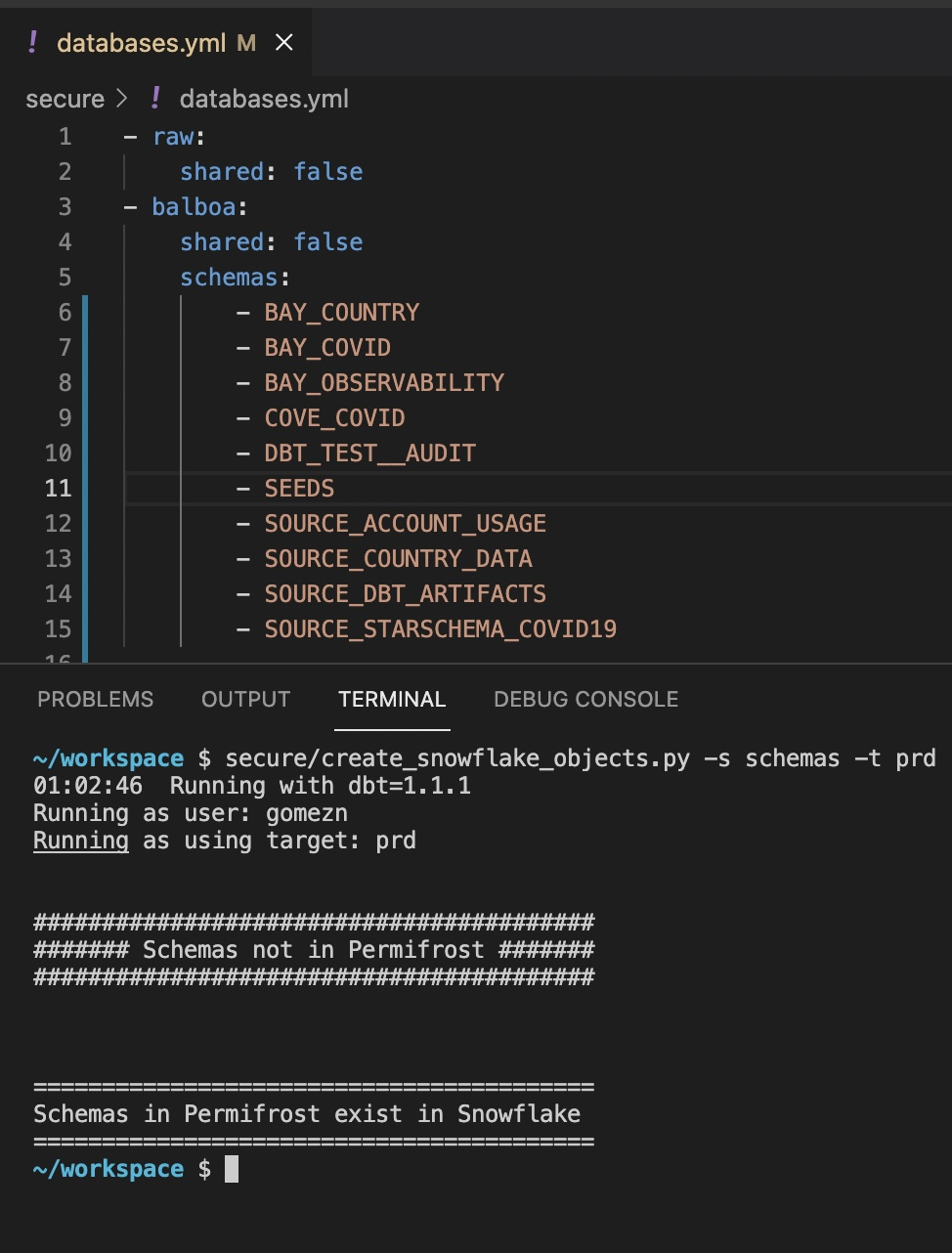
These schemas should align with what is configured in
dbt_project.yml
Role Creation
Before permifrost can be run, warehouses, schemas, and roles must already exist in Snowflake. Roles are defined in
secure/roles.yml
and created using
secure/create_snowflake_objects.py -s roles -t prd
. Note that roles will be created with the SECURITYADMIN role, so your user must have that role granted.
Roles.yml
The roles.yml file contains all the roles and their associated grants. To keep things DRY we define object roles and then assign those to higher level roles and eventually to functional roles.
Object roles are created for; warehouses, databases, schemas, and tables (we use a single role to grant access to all tables within a schema).
We follow a naming convention as follows
z_<object>_<object_name>
for example:
- z_db_raw:
- z_db_raw_write:
- z_schema_raw:
- z_schema_source_dbt_artifacts:
- z_schema_bay_country:
- z_schema_cove_covid:
- z_wh_loading:
- z_wh_transforming:
We can then "bundle" these into higher level template roles by granting the object roles.
- z_base_analyst:
member_of:
- z_db_raw
- z_db_balboa
- z_db_balboa_tst
- z_db_balboa_dev
- z_db_snowflake
- z_db_starschema_covid19
- z_schema_raw
- z_schema_snapshots
- z_schema_source_account_usage
- z_schema_source_country_data
- z_schema_source_starschema_covid19
- z_schema_seeds
- z_schema_source_dbt_artifacts
- z_schema_dbt_metrics
- z_schema_dbt_test__audit
- z_schema_bay_country
- z_schema_bay_covid
- z_schema_bay_observability
- z_schema_cove_covid
- z_wh_transforming
Finally, we can grant these template roles to functional roles modifying only the parts that make the functional roles different.
- analyst:
member_of:
- z_base_analyst
- z_tables_views_general
- z_policy_row_region_all
- analyst_pii:
member_of:
- analyst
- z_policy_unmask_pii
Here we can see that an analyst gets everything (databases, schemas, warehouses) defined in the
z_base_analyst
template role and select to all tables in those schemas via
z_tables_views_general
and all the rows related to the entire region within those tables via
z_policy_row_region_all
.
The PII Analyst just has one additional grant
z_policy_unmask_pii
which allows them to see the values within masked columns.
A German analyst is pretty similar, but can only see the German(DE) rows vs all the rows for the region.
- de_analyst:
member_of:
- z_base_analyst
- z_tables_views_general
- z_policy_row_region_de
- de_business_analyst_pii:
member_of:
- de_analyst
- z_policy_unmask_pii
Running Permifrost
To run the permifrost script, you must follow the configuration instructions at the top of the
secure/run_permifrost.sh
file and configure the predefined variables like PERMISSION_BOT_ACCOUNT.
Once the file has been configured you can run
secure/run_permifrost.sh
to apply the role permissions defined in permifrost.