How to use Datacoves Secrets Manager in Airflow
Datacoves includes a built-in
Secrets Manager
that allows you to securely store and manage secrets for both administrators and developers. Secrets can be stored at the project or environment level and easily shared across other tools in your stack, ensuring seamless integration and enhanced security.
Creating or editing a secret
in the Datacoves Secret Manager is straightforward. Be sure to prefix all secrets stored in Datacoves Secrets Manager with
datacoves-
Read variable from Datacoves Secrets manager
Once you save your variable in the Datacoves Secret Manager you are ready to use your variable in a DAG. This is done using
Variable.get
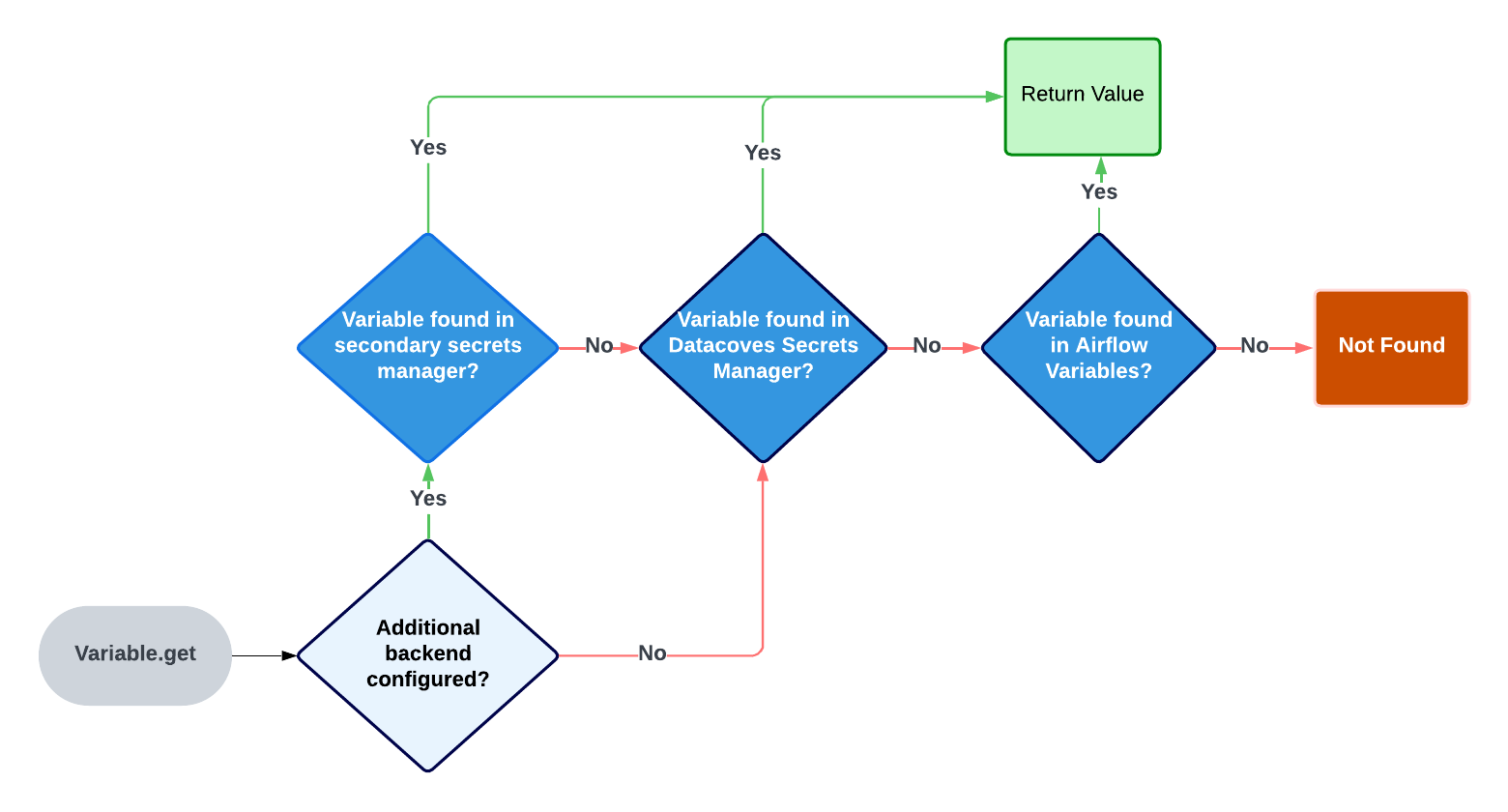
. Airflow will look in several places to find the variable.
The order of places it will look for are as follows:
- AWS Secrets Manager (If configured)
- Datacoves Secrets Manager
- Airflow variables
Once a variable is found Airflow will stop its search.
Best practices to follow when using a Secrets Manager variable
There are some best practices that we recommend when using the Datacoves Secrets manager which will improve performance and cost.
-
Always call your
Variable.getfrom within the Datacoves Task Decorators. This ensures the variable is only fetched at runtime. -
Make use of prefixes based on where your variable is stored like
datacoves-(Datacoves secrets manager will only search for secrets with this prefix),aws_,airflow_and so on to help you identify and debug your variables. eg)datacoves-mayras_secretseen in the example below.
from airflow.decorators import dag, task
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.models import Variable
doc = """## Datacoves Bash Decorator DAG
This DAG is a sample using the Datacoves decorators with variable calls."""
@dag(
default_args={
"start_date": datetime(2024, 1, 1),
"owner": "Mayra Pena",
"email": "Mayra @example.com",
"email_on_failure": True,
},
catchup=False,
tags=["version_1"],
description="Testing task decorators",
schedule_interval="0 0 1 */12 *",
)
def task_decorators_example():
@task.datacoves_bash
def calling_vars_in_decorators() -> str:
my_var = Variable.get("datacoves-mayras_secret") # Call variable within @task.datacoves_bash
return f"My variable is: {my_var}"
calling_vars_in_decorator() # Call task function
# Invoke Dag
dag = task_decorators_example()
dag.doc_md = doc
Tip
To auto mask your secret you can use
secretorpasswordin the secret name since this will sethide_sensitive_var_conn_fieldsto True. eg) aws_mayras_password. Please see this documentation for a full list of masking words.